The K35 Bronze & Iron Age Admixture Calculator
Generally, present day Eurasians, no matter whether they are from Europe or Asia are highly admixed, due to back and forth populations movements across Eurasia that have occurred over the past 5000 years.
Europeans have inherited considerable DNA from ancient Asian populations, and similarly Asians have also inherited considerable DNA from ancient European populations. This ADMIXTURE based calculator which we believe is the best of its kind will help you decipher some of your ancient genetic connections to other parts of the world.
The flood of recently sequenced ancient DNA (aDNA) has tremendously increased our understanding of demography of various Eurasian modern populations. This K36 calculator based on ADMIXTURE software, seeks to model present day individuals based on primarily ancient populations from the Bronze and Iron Age.
The test creator, who has a website; EurasianDNA.com, has extensive experience with bioinformatics and statistics related software and tests. He has “fine-tuned” this calculator to output accurate admixture models. To reduce margins of error, he only uses ancient DNA samples with higher average read depths, for component references.
One of the challenges in creating accurate tests using a DNA is that there is sometimes inadequate SNP overlap between the tester’s DNA and the aDNA samples. Thus for this test, users who have been genotyped using the Illumina V5 chip, such as newer 23andMe customers LivingDNA customers will experience higher margins of error with this calculator. Older 23andMe customers who were genotyped with the Illumina V3 or V4 chip should be fine.
Macro-Populations
The references for this calculator can be grouped into macro-populations as follows:
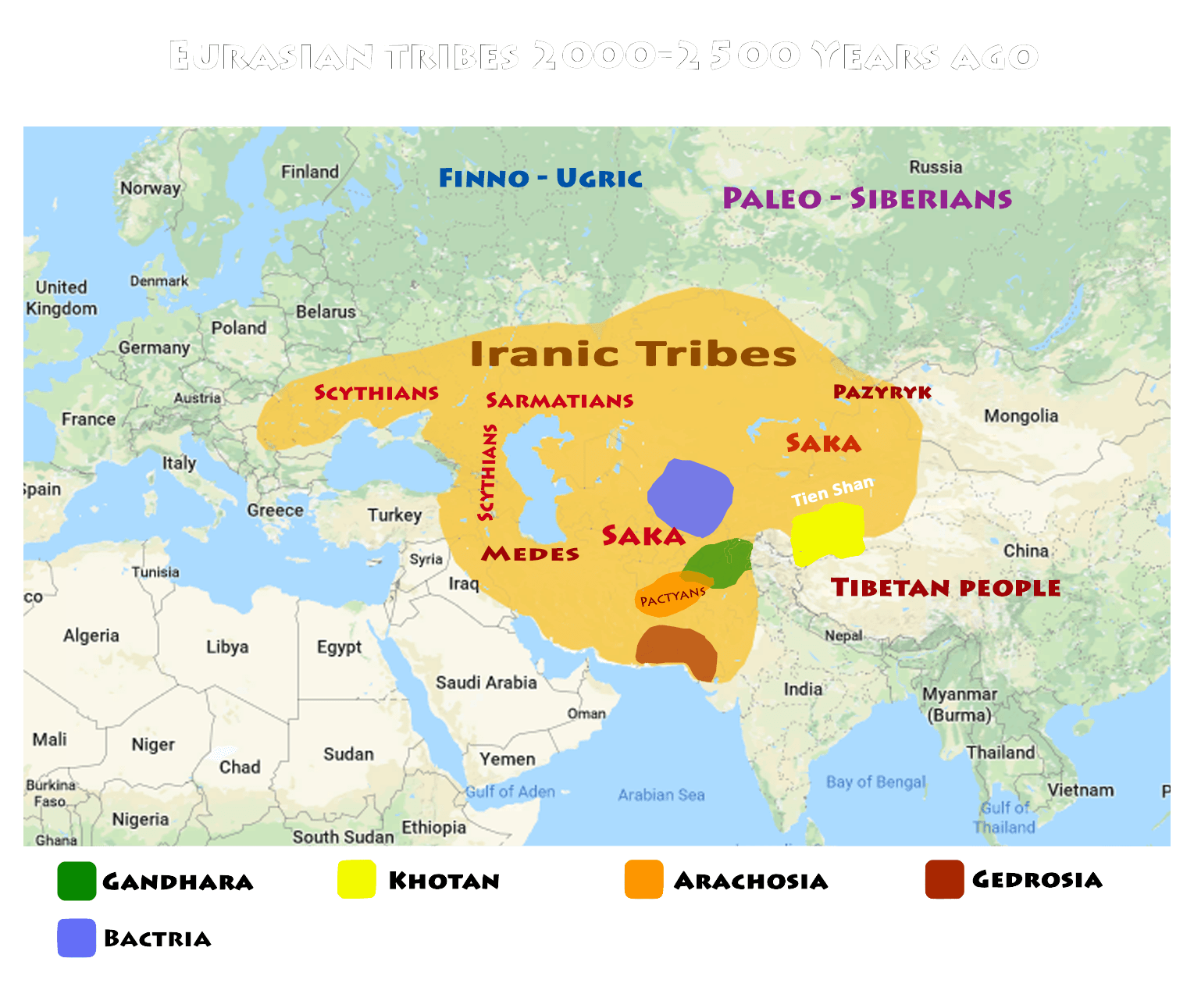
Scythians/Huns/Saka
These are the warrior nomads who roamed the Eurasian Steppe and Central Asia during the Iron Age (IA). They most likely spoke an Indo-Iranian language and had an impact on the demography of Europeans and West and South Asians. Their genetic impact on Europeans was via related groups such as the Alans and Bulgars. Their impact on Eastern Europe and the Caucasus was greatest between the 4th and 6th centuries AD.
The Sarmatians were an Iranic peoples originating in Central Asia, and were closely related to the Scythians. They flourished from the 5th century BC to the 4th century AD. They started dominating the Scythians by around 200 BC. At their zenith, they ranged from the Vistula River to the mouth of the Danube and eastward to the Volga, bordering the shores of the Black and Caspian seas as well as the Caucasus to the south.
Bactria Margiana Archaeological Complex (BMAC)
Also known as the Oxus civilization, the BMAC is a Bronze Age (4000 year old) which ranged from Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan to Tajikistan in Central Asia. They were wheat and barley agriculturalists.
Genetically they derived from Iranian farmers, similar to Tepe-Hissar, with smaller inputs from Western Siberian hunter gatherers and Ancestral South Indians. In this calculator the references are represented by Dzharkutan-BA and Sappali-Tepe-BA from Uzbekistan. They traded with and had cultural contacts with the Indus Valley Civilization and Bronze Age Iranians.
Indus Valley Civilization (IVC)
Situated in present day Pakistan and India, the IVC or Harappan civilization, was a Bronze Age. Changing monsoon patterns aridified the area and likely led to their demise.
In this calculator, the references are represented by closely related Iron Age samples from the Swat area of Pakistan. They include Loebanr, Saidu Sharif, and Udegram.
Steppe-MLBA-Eastern
These include various Bronze Age groups from the Kazakhstan area on the Eurasian Steppe. In this calculator they include groups such Maitan, Krasnoyarsk_MLBA and Zevakinsky. These groups derive most of their ancestry from Steppe-MLBA-Western groups with an added layer of about 25% E Asian related ancestry.
Ancient Ancestral South Indians (AASI)
Present day South Asians can be modeled as a mixture of the endigenous Indians who followed the coastal route from Arabia to India around 40,000 years ago; AASI, and peoples related to the Neolithic Iranian farmers from the Zagros mountains area, and Iron Age Saka related populations from the Eurasian steppe.
Here AASI is represented by a combination of the endangered Onge tribe from the Andaman Islands, and South Indian tribals; Paniya and Korwa.
African
Due to a lack of appropriate ancient African sources, modern Africans are used as references as follows:
African-W; Yorubans and Gambians
African-E; Masai tribe
African-E2; Hadza tribe
African-S; Mbuti and Jo-Hoan tribes
Other components
Iranian farmers from the Chalcolithic played a key role in the population histories of both West and South Asia. Here they are represented by Iran-Chl and Haji-Firuz-Chl references.
The Kura-Araxes culture which disappeared around 4500 years ago, thrived in an area extending from eastern Turkey to north-western Iran. Here they are represented by Armenia-BA references.
Present day Cambodians are used as references for E Asian related admixture. The decision to use Cambodians is due to a lack of a good ancient source for E Asian admixture. There are Siberian Baikal Hunter Gatherer ancient samples from the Neolithic, however, the SNP overlap with current commercial micro-arrays is not high enough.
Native Americans are represented by the Karitiana tribe from South America.
Abbreviations:
BA – Bronze Age
EBA – Early Bronze Age
MLBA – Middle to Late Bronze Age
LBA – Late Bronze Age
IA – Iron Age
Chl- Chalcolithic
References:
1. The first horse herders and the impact of early Bronze Age steppe expansions into Asia, Peter de Barros Damgaard et al., 2018.
2. The Genomic Formation of South and Central Asia, Vagheesh M. Narasimhan et al., 2018.
3. The population genomics of archaeological transition in west Iberia: Investigation of ancient substructure using imputation and haplotype-based methods, Rui Martiniano et al., 2017.
3. The Beaker Phenomenon And The Genomic Transformation Of Northwest Europe, Olaide et al., 2017.
3. Genome-wide patterns of selection in 230 ancient Eurasians, Mathieson et al., 2015.
Calculator:
https://www.geneplaza.com/app-store/69/preview